
You can verify a promissory note by checking with the Securities and Exchange Commission’s EDGAR database. Structured notes have complex principal protection that offers investors lower risk, but keep in mind that these notes are not risk-free. The risk of a note ultimately depends on the issuer’s creditworthiness. According to the calculations, the total amount due on May 1st will be the principal amount plus interest payable. The principal of $10,475 due at the end of year 4—within one year—is current.
What happens when a company pays off notes payable?
The company makes a corresponding “furniture” entry in the asset account. Notes payable represent a formal contract between a borrower and a lender. It consists of a written promise to repay a loan, usually specifying the principal amount, interest to be paid, and a due date.
What is a Note Payable? (Definition, Nature, Example, and Journal Entries)
- The first journal is to record the principal amount of the note payable.
- In a company’s balance sheet, the total debits and credits must equal or remain “balanced” over time.
- On the other hand, accounts payable are debts that a company owes to its suppliers.
- A low interest rate is possible for borrowers with a strong credit and financial profile.
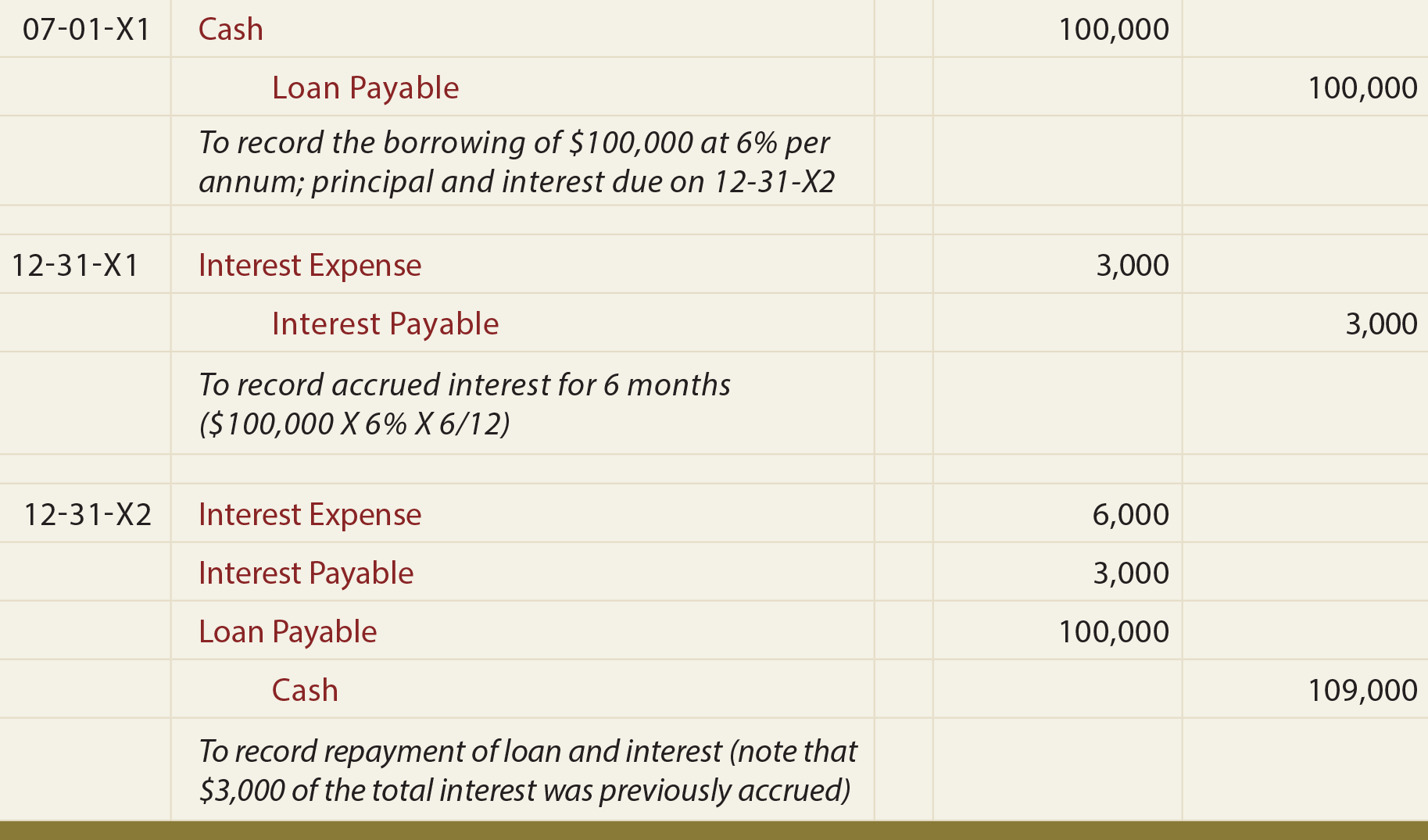
A note payable is a loan contract that specifies the principal (amount of the loan), the interest rate stated as an annual percentage, and the terms stated in number of days, months, or years. A note payable may be either short term (less than one year) or long term (more than one year). They can be found in current liability when the balance is due within one year. They would be classified under long-term liabilities in the balance sheet if the note’s maturity is after a year. The long term-notes payable are very similar to bonds payable because their principle amount is due on maturity but the interest thereon is usually paid during the life of the note.
Similarities Between Accounts Payable and Notes Payable
Accounts Payable refers to the amount a company owes suppliers when goods are purchased or services are availed on credit. It is a current liability account that usually has a credit balance and represents amounts due to suppliers and vendors. It has agreed-upon terms and conditions that must be satisfied to honor the agreement. However, the account payables are informal is notes payable an asset records, and the terms & conditions are not rigid. Since they’re not written agreements, the terms can be changed on the agreement between the vendor and the business entity. If a debtor runs into financial difficulties and is unable to pay, or fully repay, the note, the estimated impaired cash flows become an important reporting disclosure for the lender.
Businesses use this account in their books to record their written promises to repay lenders. Likewise, lenders record the business’s written promise to pay back funds in their notes receivable. Notes payable are required when a company borrows money from a bank or other lender. Notes payable may also be part of a transaction to acquire expensive equipment. In certain cases, a supplier will require a note payable instead of terms such as net 30 days. On its balance sheet, the company records the loan as notes payable.
Part 2: Your Current Nest Egg
If the loan due date is within 12 months, it’s considered a short-term liability. A retail store orders and receives $10,000 of merchandise from a supplier. The supplier offers 30-day payment terms, which means the retail store has 30 days to pay the outstanding amount. In this case, the retail store would record the $10,000 as accounts payable, a current liability on the balance sheet. Since no written promissory note is involved, it falls under accounts payable. Notes payable and accounts payable play an essential role in a business’s financial management.
Short-term debt obligations to suppliers and creditors that support normal business operations, representing money owed for goods or services received on credit. To understand the differences between notes payable and accounts payable, let’s delve deeper into this. Continuing with the above example, let’s assume the loan company applied to buy that vehicle is from Bank of America. The promissory note is payable two years from the initial issue of the note, which is dated January 1, 2021, so the note would be due December 31, 2023. Once you create a note payable and record the details, you must record the loan as a note payable on your balance sheet (which we’ll discuss later).
The journal entries for notes payable related to equipment, inventory, or account payable will also be similar to how we have made entries above. One thing to be noted for the notes payable is that the interest payable or interest liability has not been recorded in the first entry. It’s because the interest amount was not due on the date of loan issuance. The due date and allowed period are also mentioned on the note payable.
The notes payable are not issued to general public or traded in the market like bonds, shares or other trading securities. They are bilateral agreements between issuing company and a financial institution or a trading partner. The company ABC receives the money on the signing date and as agreed in the note, it is required to back both principal and interest at the end of the note maturity.
These examples show the practical application of accounts payable and notes payable in everyday business scenarios. Understanding the differences between the two is essential for accurate financial record-keeping and decision-making. An established restaurant upgrades its kitchen equipment and purchases $20,000 worth of appliances from a vendor. The vendor provides the restaurant with a financing option, allowing the restaurant to pay for the equipment in installments over two years with an agreed-upon interest rate. In this case, the restaurant would record this transaction as notes payable, as it involves a written agreement detailing the payment terms and interest charges.
A note payable can be defined as a written promise to pay a sum of the amount on the future date for the services or product. Secured notes payable identify collateral security in the form of assets belonging to the borrower that the creditor can seize if the note is not paid at the maturity date. On the maturity date, both the Note Payable and Interest Expense accounts are debited.